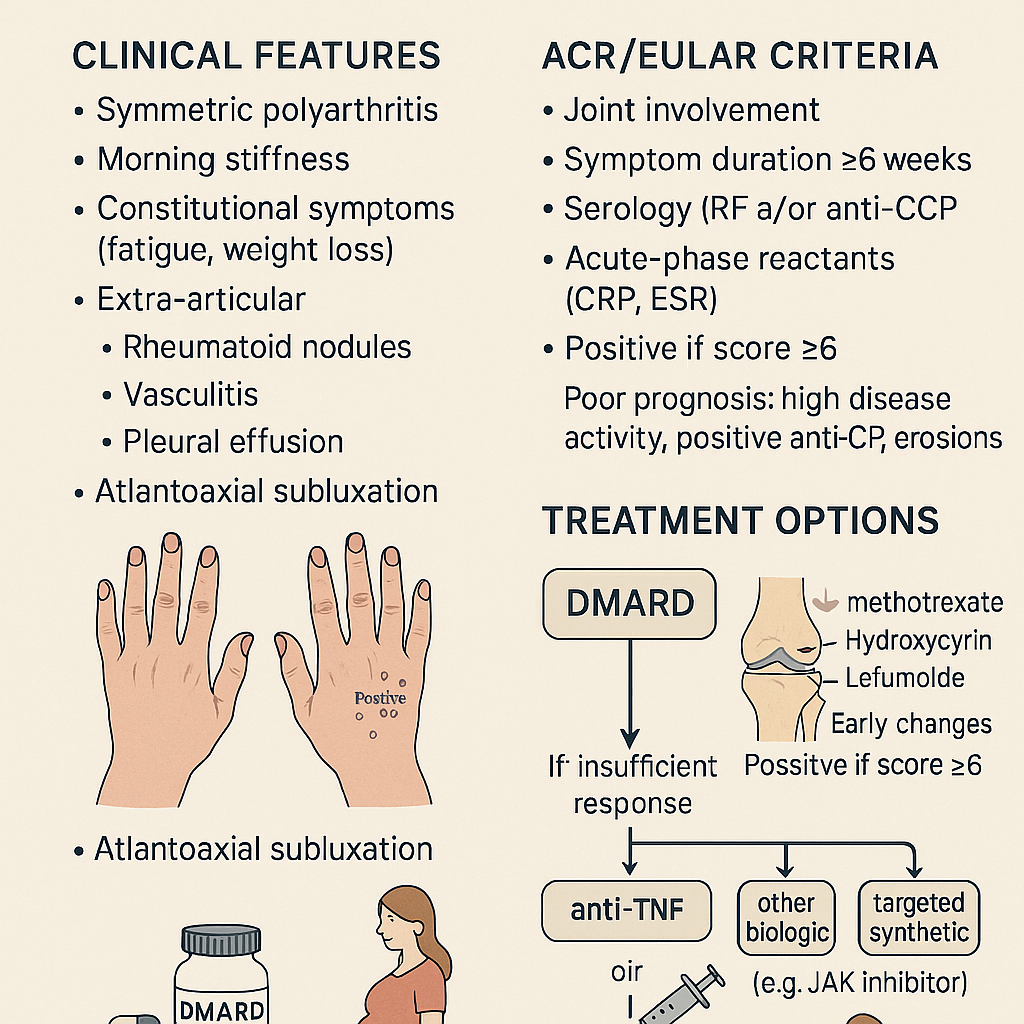
Rheumatoid Arthritis: Clinical Features, ACR/EULAR Criteria & Treatment Options
Explore Related Content
- Home Latest medical posts
- Sitelinks Index Complete site map
- Upload Medical Content Share clinical pearls
- More medicine Posts Browse related content
- Reviews & Suggestions Community feedback
- Help & FAQ Upload & SEO tips
- More from this Author View all posts
- About Streamora Medical learning hub
Related Posts
Posts with similar category or tags for stronger sitelinks & internal backlinks.
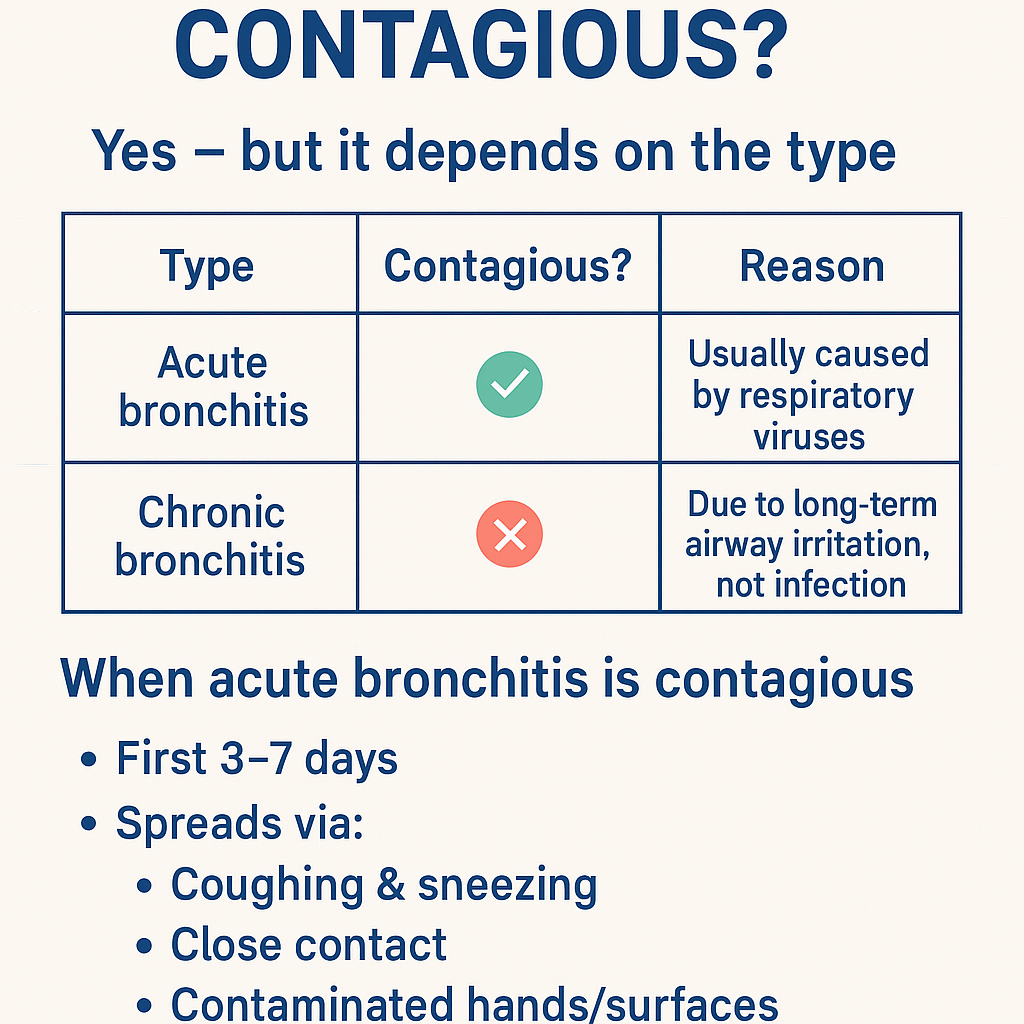
Is bronchitis contagious ? Bronchitis: Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis, Contagiousness & Complete Treatment Guide (Acute vs Chronic)
Got it 👍 — **no images in chat**. Below is a **complete, concise-but-exhaustive medical reference on BRONCHITIS**, exactly in the structured style you prefer. --- # **Is Bronchitis Contagious?** ### **Yes — but it depends on the type** | Type | Contagious? | Reason | | ---------------------- | ----------- | ----------------------------------------------------- | | **Acute bronchitis** | ✅ **Yes** | Usually caused by **respiratory viruses** | | **Chronic bronchitis** | ❌ **No** | Due to **long-term airway irritation**, not infection | ### **When acute bronchitis is contagious** * First **3–7 days** * Spreads via: * Coughing & sneezing * Close contact * Contaminated hands/surfaces --- # **BRONCHITIS – COMPLETE MEDICAL GUIDE** --- ## **1. Definition** **Bronchitis** is **inflammation of the bronchial tubes**, causing **cough with or without sputum, wheeze, and airflow limitation**. --- ## **2. Classification** ### **A. Acute Bronchitis** * Sudden onset * Duration: **<3 weeks** * Usually **viral** ### **B. Chronic Bronchitis (COPD subtype)** * Productive cough for **≥3 months in 2 consecutive years** * Non-infectious * Progressive disease --- ## **3. Pathophysiology** ### Acute Bronchitis * Viral infection → epithelial injury * Inflammatory mediators → mucosal edema * Increased mucus → impaired ciliary clearance * Transient bronchoconstriction ### Chronic Bronchitis * Chronic irritant exposure → goblet cell hyperplasia * Excess mucus → airway plugging * Reduced ventilation → hypoxia & hypercapnia * Leads to **COPD** --- ## **4. Etiology / Causes** ### **Acute Bronchitis** * **Viruses (≈90%)** * Influenza * Rhinovirus * RSV * Coronavirus * **Atypical bacteria (rare)** * *Mycoplasma pneumoniae* * *Chlamydia pneumoniae* * Risk factors: * Smoking * Air pollution * Crowded environments ### **Chronic Bronchitis** * Cigarette smoking (most common) * Biomass fuel exposure * Occupational dust & chemicals * Recurrent infections --- ## **5. Clinical Features** ### **Acute Bronchitis** * Persistent **cough** (dry → productive) * Mucoid or purulent sputum * Low-grade fever * Chest tightness * Wheeze * Mild dyspnea * Malaise, fatigue ### **Chronic Bronchitis** * Daily productive cough * Thick sputum * Dyspnea on exertion * Cyanosis (“blue bloater”) * Peripheral edema (cor pulmonale) * Frequent exacerbations --- ## **6. Investigations** ### Acute Bronchitis * **Clinical diagnosis** * Chest X-ray → only if: * High fever * Tachypnea * Focal chest signs * CBC usually normal ### Chronic Bronchitis * **Spirometry** * ↓ FEV1 * ↓ FEV1/FVC * Chest X-ray: * Increased bronchovascular markings * ABG (advanced): * Hypoxemia * Hypercapnia * Sputum culture (exacerbations) --- ## **7. Differential Diagnosis** * Pneumonia * Asthma * COPD exacerbation * Pulmonary embolism * Tuberculosis (important in India) * Heart failure --- ## **8. Management** --- ## **A. Acute Bronchitis** ### **1️⃣ Non-pharmacological** * Rest * Adequate hydration * Warm fluids * Humidified air * Avoid smoking ### **2️⃣ Pharmacological** #### **Antipyretic / Analgesic** **Paracetamol** * Dose: 500–1000 mg every 6–8 h (max 4 g/day) * MOA: Central COX inhibition * Adverse effects: Hepatotoxicity (overdose) * Counselling: Avoid alcohol excess #### **Bronchodilator (if wheeze)** **Salbutamol** * Dose: 2–4 puffs every 4–6 h * MOA: β2-agonist → bronchodilation * Side effects: Tremor, palpitations * Monitoring: Heart rate #### **Antibiotics** ❌ **NOT routinely indicated** * Use only if: * Suspected bacterial infection * Elderly/comorbid * Prolonged symptoms **Amoxicillin / Azithromycin** (if indicated) --- ## **B. Chronic Bronchitis** ### **1️⃣ Lifestyle** * **Smoking cessation (most important)** * Vaccinations: * Influenza * Pneumococcal ### **2️⃣ Pharmacological** * **Bronchodilators** * SABA / LABA * **Inhaled corticosteroids** (selected patients) * **Mucolytics** * **Antibiotics** during infective exacerbations * **Oxygen therapy** (chronic hypoxemia) --- ## **9. Complications** ### Acute * Secondary pneumonia * Bronchospasm * Prolonged cough ### Chronic * COPD progression * Pulmonary hypertension * Cor pulmonale * Respiratory failure --- ## **10. Prevention** * Hand hygiene * Mask during respiratory infections * Smoking cessation * Avoid air pollution * Vaccinations --- ### **Key Exam Pearls** * Acute bronchitis → **viral, self-limiting** * Green sputum ≠ bacterial infection * Chronic bronchitis = **COPD** * Antibiotics are **not first-line** --- If you want next: * **SEO title, description & keywords** * **Case-based MCQs** * **Flowchart-style management** * **Comparison table: bronchitis vs pneumonia vs asthma** Just tell me ✔️
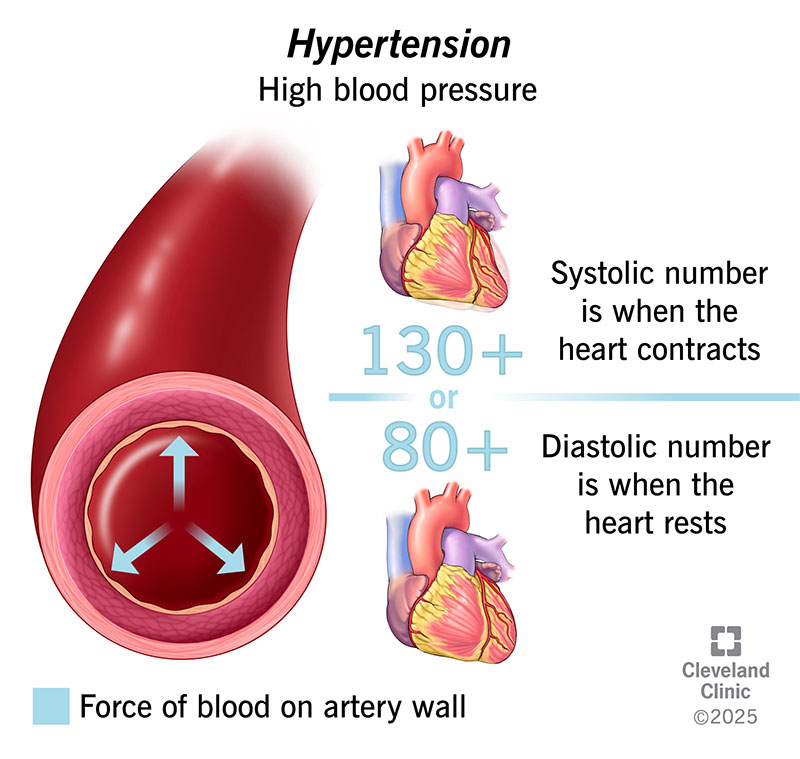
What Causes High Blood Pressure? Common Reasons, Risk Factors & Hidden Causes Explained
High blood pressure (**hypertension**) develops when the force of blood pushing against artery walls stays too high over time. It usually results from a **combination of causes and risk factors**, not a single reason. --- ## 🔹 Main Causes of High Blood Pressure ### 1️⃣ **Primary (Essential) Hypertension** – *Most common* * No single identifiable cause * Develops gradually over years * Strongly linked to lifestyle and genetics --- ### 2️⃣ **Secondary Hypertension** – *Due to an underlying condition* Caused by a specific medical problem and often appears suddenly. **Common causes include:** * **Kidney disease** (CKD, renal artery stenosis) * **Hormonal disorders** * Hyperaldosteronism * Cushing syndrome * Pheochromocytoma * Thyroid disorders * **Obstructive sleep apnea** * **Pregnancy-related hypertension** * **Certain medications** * NSAIDs * Oral contraceptives * Steroids * Decongestants --- ## 🔹 Major Risk Factors ### 🧬 **Non-modifiable** * Family history (genetics) * Increasing age * Male sex (younger age), females (post-menopause) ### 🧂 **Modifiable (Lifestyle-related)** * High salt (sodium) intake * Obesity and overweight * Physical inactivity * Excess alcohol intake * Smoking * Chronic stress * Poor sleep --- ## 🔹 How These Factors Raise Blood Pressure * **Narrowing of blood vessels** → increased resistance * **Increased blood volume** (salt & fluid retention) * **Overactive sympathetic nervous system** * **Hormonal imbalance** (RAAS activation) --- ## 🔹 Key Takeaway > **High blood pressure is usually caused by long-term lifestyle factors combined with genetic susceptibility, but sometimes it is a warning sign of another disease.** --- If you want, I can also provide: * ✅ **Causes by age group** * ✅ **Flowchart of hypertension pathophysiology** * ✅ **Difference between primary vs secondary hypertension** * ✅ **When to suspect secondary hypertension** Just tell me 👍
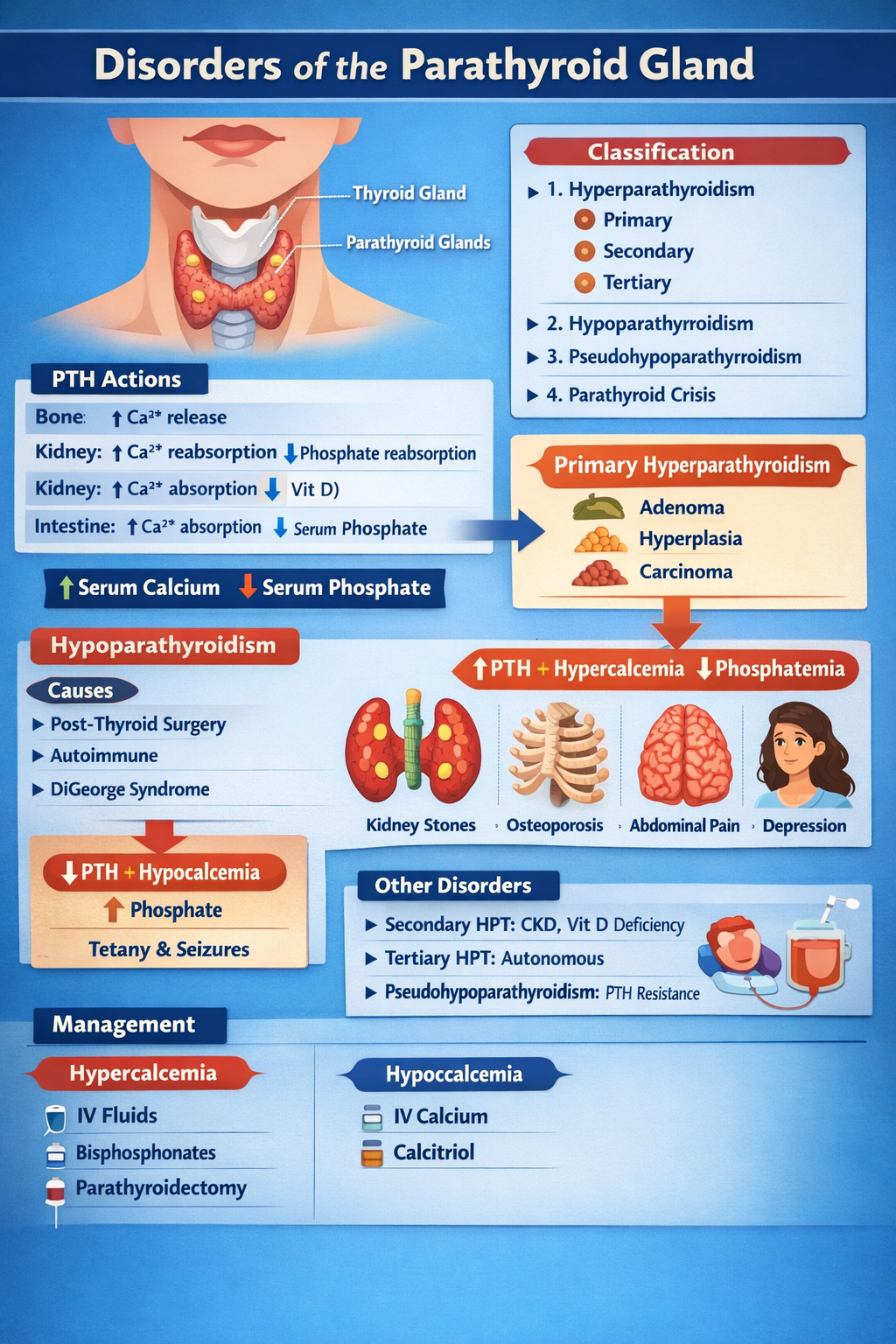
Disorders of Parathyroid Gland Complete Clinical Guide for Medical Students
--- # **DISORDERS OF THE PARATHYROID GLAND** --- ## **1. Physiology of Parathyroid Hormone (PTH)** **Parathyroid glands (4)** → secrete **PTH** → maintain **serum calcium and phosphate balance** ### **Normal actions of PTH** | Target organ | Action | | ------------- | ----------------------------------------------- | | **Bone** | ↑ Osteoclastic bone resorption → ↑ Ca²⁺ release | | **Kidney** | ↑ Ca²⁺ reabsorption, ↓ phosphate reabsorption | | **Kidney** | ↑ 1-α hydroxylase → ↑ calcitriol | | **Intestine** | Indirectly ↑ Ca²⁺ absorption via vitamin D | **Net effect:** **↑ Serum calcium, ↓ serum phosphate** --- # **CLASSIFICATION** 1. **Hyperparathyroidism** * Primary * Secondary * Tertiary 2. **Hypoparathyroidism** 3. **Pseudohypoparathyroidism** 4. **Parathyroid crisis** --- # **PRIMARY HYPERPARATHYROIDISM (PHPT)** ## **Definition** Autonomous excessive PTH secretion → **hypercalcemia** ## **Causes** | Cause | % | | ----------------------- | ------ | | Parathyroid adenoma | 85% | | Parathyroid hyperplasia | 10–15% | | Parathyroid carcinoma | <1% | | MEN-1, MEN-2A | Rare | --- ## **Pathophysiology** Excess PTH → * ↑ Bone resorption → osteoporosis * ↑ Renal Ca reabsorption * ↑ Vitamin D → ↑ gut Ca absorption → **Hypercalcemia + hypophosphatemia** --- ## **Clinical Features** **“Stones, Bones, Groans, Thrones, Psychiatric Overtones”** | System | Features | | ------ | ---------------------------------------------- | | Kidney | Nephrolithiasis, polyuria | | Bone | Bone pain, fractures, osteitis fibrosa cystica | | GIT | Constipation, pancreatitis, peptic ulcer | | CNS | Depression, confusion | | Heart | Short QT | --- ## **Investigations** | Test | Result | | -------------------- | ---------------- | | Serum Ca | ↑ | | Serum phosphate | ↓ | | PTH | ↑ | | ALP | ↑ | | 24-hr urine Ca | ↑ | | DEXA | Osteoporosis | | Neck USG / Sestamibi | Localize adenoma | --- ## **Differential Diagnosis** | Condition | PTH | Ca | | ------------------------ | --- | -------- | | PHPT | ↑ | ↑ | | Malignancy hypercalcemia | ↓ | ↑ | | FHH | ↑ | Normal/↑ | --- ## **Management** ### **A. Acute hypercalcemia** | Step | Treatment | | ---- | ----------------- | | 1 | IV normal saline | | 2 | Loop diuretic | | 3 | IV bisphosphonate | | 4 | Calcitonin | ### **B. Definitive** **Parathyroidectomy** **Indications** * Ca >1 mg/dL above normal * Kidney stones * Osteoporosis * Age <50 --- # **SECONDARY HYPERPARATHYROIDISM** ## **Definition** Compensatory ↑ PTH due to **hypocalcemia** ## **Causes** * Chronic kidney disease (most common) * Vitamin D deficiency * Malabsorption --- ## **Biochemistry** | Parameter | Result | | --------- | ---------- | | Calcium | ↓ | | Phosphate | ↑ (in CKD) | | PTH | ↑ | | Vitamin D | ↓ | --- ## **Management** * Oral calcium * Vitamin D (calcitriol) * Phosphate binders * Dialysis if CKD --- # **TERTIARY HYPERPARATHYROIDISM** Long-standing secondary → autonomous glands | Ca | PTH | | -- | --- | | ↑ | ↑ | **Treatment:** Parathyroidectomy --- # **HYPOPARATHYROIDISM** ## **Definition** Deficient PTH → hypocalcemia ## **Causes** * Post-thyroid surgery (most common) * Autoimmune * DiGeorge syndrome * Hypomagnesemia --- ## **Pathophysiology** Low PTH → ↓ calcium, ↑ phosphate → neuromuscular excitability --- ## **Clinical Features** | Feature | Mechanism | | --------------- | ------------------------------ | | Tetany | Hypocalcemia | | Chvostek sign | Facial nerve hyperexcitability | | Trousseau sign | Carpopedal spasm | | Seizures | Low Ca | | QT prolongation | Hypocalcemia | --- ## **Investigations** | Test | Result | | --------- | -------- | | Ca | ↓ | | Phosphate | ↑ | | PTH | ↓ | | Mg | May be ↓ | --- ## **Management** ### **Acute** IV **calcium gluconate** ### **Chronic** * Oral calcium * Calcitriol --- # **CALCIUM GLUCONATE** | Parameter | Value | | ------------ | -------------------- | | Indication | Acute tetany | | Mechanism | Raises serum Ca | | Dose | 10 ml of 10% IV slow | | Side effects | Arrhythmia | | Monitoring | ECG | --- # **CALCITRIOL (Vitamin D)** | Feature | Detail | | ------------ | -------------------------- | | Action | ↑ Intestinal Ca absorption | | Dose | 0.25–1 mcg/day | | Side effects | Hypercalcemia | | Monitoring | Serum Ca | --- # **PSEUDOHYPOPARATHYROIDISM** ## **Definition** Target organ resistance to PTH | Ca | PTH | Phosphate | | -- | --- | --------- | | ↓ | ↑ | ↑ | ## **Clinical** * Short stature * Round face * Brachydactyly * Mental retardation **Treatment:** Calcium + Vitamin D --- # **PARATHYROID CRISIS** Severe hypercalcemia (>14 mg/dL) ### **Features** * Dehydration * Arrhythmia * Coma ### **Management** 1. IV saline 2. Loop diuretic 3. Calcitonin 4. Bisphosphonates 5. Dialysis if refractory --- # **EXAM PEARLS** | Scenario | Diagnosis | | --------------------------------- | --------------------------- | | High Ca + high PTH | Primary hyperparathyroidism | | Low Ca + high PTH | Secondary HPT | | Low Ca + low PTH | Hypoparathyroidism | | Low Ca + high PTH + short fingers | Pseudohypoparathyroidism | ---
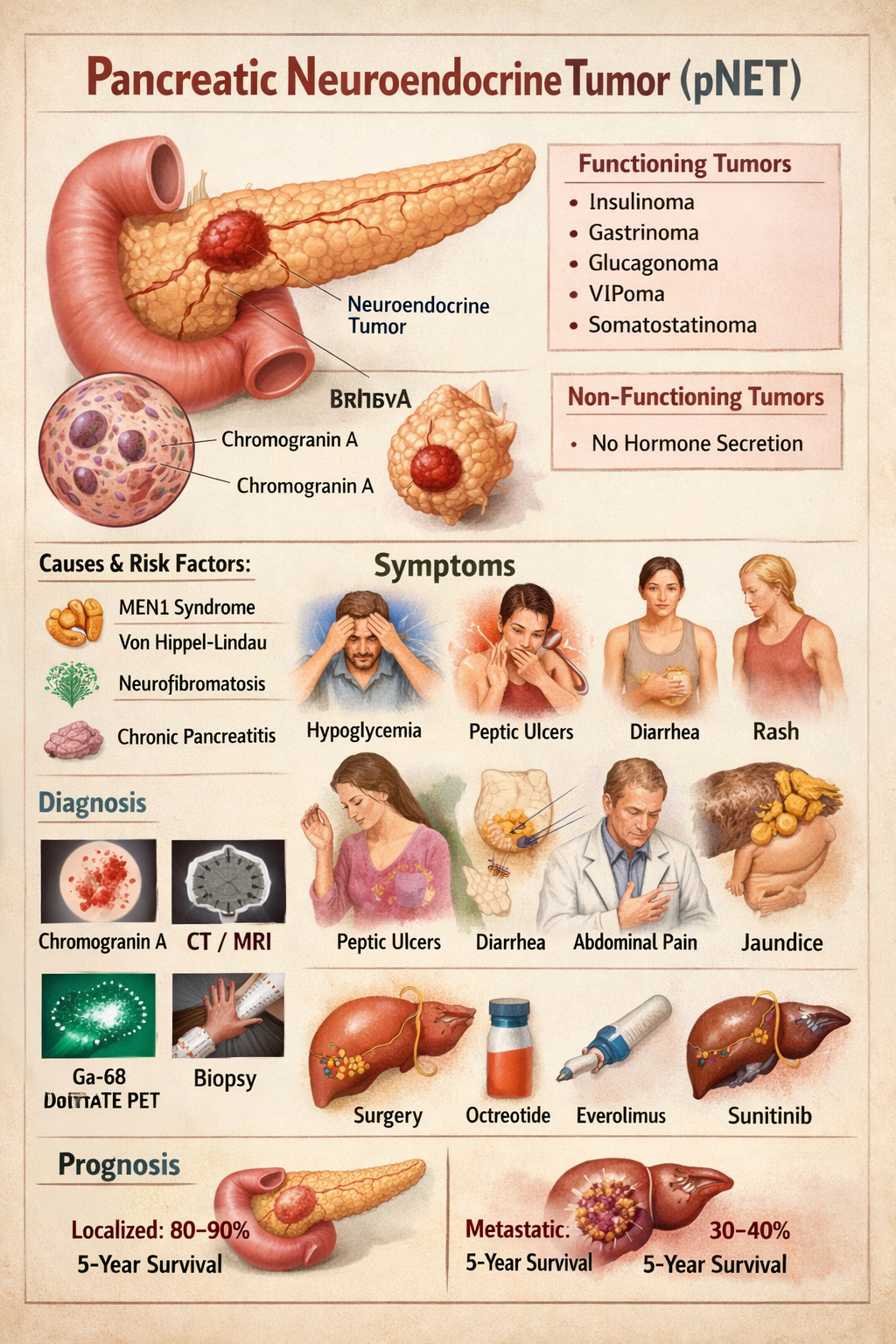
Pancreatic Neuroendocrine Tumor Symptoms Diagnosis Treatment Prognosis
--- # **PANCREATIC NEUROENDOCRINE TUMOR (pNET)** --- ## **1. Definition** Pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors (pNETs) are **neoplasms arising from endocrine (islet) cells of the pancreas** that secrete peptide hormones or amines. They are biologically distinct from pancreatic adenocarcinoma and may be **functioning (hormone-secreting)** or **non-functioning**. --- ## **2. Pathophysiology** pNETs originate from **enterochromaffin cells** of pancreatic islets. They show: * **Neuroendocrine differentiation** * **Dense-core secretory granules** * **Expression of chromogranin A and synaptophysin** Tumor behavior depends on: * **Hormone secretion** * **Tumor size** * **Ki-67 index (mitotic rate)** * **Invasion and metastasis** Tumors may be: * **Well differentiated (NET G1–G3)** * **Poorly differentiated (Neuroendocrine carcinoma)** MEN1 mutation commonly involved → parathyroid, pituitary, pancreas tumors. --- ## **3. Classification** ### **A. By hormone secretion** | Type | Hormone | | --------------- | ------------ | | Insulinoma | Insulin | | Gastrinoma | Gastrin | | Glucagonoma | Glucagon | | VIPoma | VIP | | Somatostatinoma | Somatostatin | | Non-functioning | None | ### **B. By WHO grading** | Grade | Ki-67 | | ----- | ----- | | G1 | <3% | | G2 | 3–20% | | G3 | >20% | --- ## **4. Causes and Risk Factors** * MEN-1 syndrome * Von Hippel–Lindau * Neurofibromatosis-1 * Tuberous sclerosis * Smoking * Chronic pancreatitis --- ## **5. Clinical Features** ### **A. Insulinoma** * Hypoglycemia * Sweating * Palpitations * Confusion * Weight gain ### **B. Gastrinoma (Zollinger-Ellison)** * Severe recurrent peptic ulcers * Diarrhea * GERD ### **C. Glucagonoma** * Diabetes * Necrolytic migratory erythema * Weight loss * Anemia ### **D. VIPoma** * Profuse watery diarrhea * Hypokalemia * Achlorhydria ### **E. Somatostatinoma** * Diabetes * Gallstones * Steatorrhea ### **F. Non-functioning** * Abdominal pain * Weight loss * Jaundice * Abdominal mass * Metastasis symptoms --- ## **6. Investigations** ### **Blood Tests** | Test | Use | | ------------------ | --------------- | | Chromogranin-A | Tumor marker | | Insulin, C-peptide | Insulinoma | | Gastrin | Gastrinoma | | Glucagon | Glucagonoma | | VIP | VIPoma | | Somatostatin | Somatostatinoma | | Fasting glucose | Hypoglycemia | ### **Imaging** * Contrast CT * MRI pancreas * Endoscopic ultrasound (best for small tumors) * Ga-68 DOTATATE PET-CT (gold standard) * Octreoscan ### **Biopsy** * EUS-guided biopsy * Ki-67 index --- ## **7. Differential Diagnosis** * Pancreatic adenocarcinoma * Islet cell hyperplasia * Metastatic carcinoid * Chronic pancreatitis * Insulin autoimmune syndrome --- ## **8. Management** ### **A. Curative – Surgery** * Enucleation (small insulinomas) * Distal pancreatectomy * Whipple procedure * Liver metastasis resection ### **B. Medical Therapy** Used when metastatic, unresectable or hormone excess. --- ## **9. Drugs Used** ### **1. Octreotide** **Indication:** Hormone control and tumor stabilization **Mechanism:** Somatostatin analog → inhibits hormone secretion **Dose:** Adult: 100–500 mcg SC 2–3 times/day or 20–30 mg IM monthly Paediatric: 1–10 mcg/kg/day **Adverse effects:** Gallstones, diarrhea, hyperglycemia **Contraindication:** Severe gallbladder disease **Monitoring:** LFT, glucose **Counsel:** May cause GI upset --- ### **2. Lanreotide** Same as octreotide Dose: 120 mg SC every 4 weeks --- ### **3. Everolimus** **Indication:** Advanced pNET **Mechanism:** mTOR inhibitor **Dose:** 10 mg daily **Adverse:** Mouth ulcers, hyperglycemia, infections **Contra:** Active infection **Monitor:** CBC, glucose **Counsel:** Avoid live vaccines --- ### **4. Sunitinib** **Indication:** Metastatic pNET **Mechanism:** VEGF receptor inhibitor **Dose:** 37.5 mg daily **Adverse:** Hypertension, fatigue **Contra:** Cardiac failure **Monitor:** BP, ECG --- ### **5. Diazoxide (for insulinoma)** **Mechanism:** Inhibits insulin release **Dose:** 100–600 mg/day **Adverse:** Fluid retention, hyperglycemia **Monitor:** Glucose, edema --- ### **6. Streptozocin + 5-FU (Chemotherapy)** **Indication:** High-grade metastatic disease **Adverse:** Nephrotoxicity, nausea --- ## **10. Non-Pharmacologic** * Surgical resection * Radiofrequency ablation of liver mets * Peptide receptor radionuclide therapy (PRRT) * Dietary glucose support in insulinoma --- ## **11. Prognosis** * Localized pNET: 80–90% 5-year survival * Metastatic: 30–40% Better than pancreatic adenocarcinoma --- ## **12. Key Exam Points** * Insulinoma = most common pNET * Gastrinoma = most malignant * MEN1 = 3 P’s: Parathyroid, Pituitary, Pancreas * Chromogranin A is universal tumor marker * Ga-68 DOTATATE PET = best imaging ---
Comments & Discussion
Use this thread like a mini viva: add differentials, staging systems, drug regimens and exam tricks.
Login or register to comment.